Default Arguments
When we mention a default value for a parameter while declaring the function, it is said to be as default argument. In this case, even if we make a call to the function without passing any value for that parameter, the function will take the default value specified.
sum(int x, int y=0)
{
cout << x+y;
}
Here we have provided a default value for y, during function definition.
int main()
{
sum(10);
sum(10,0);
sum(10,10);
}
10 10 20
First two function calls will produce the exact same value.
for the third function call, y will take 10 as value and output will become 20.
By setting default argument, we are also overloading the function. Default arguments also allow you to use the same function in different situations just like function overloading.
The idea behind default argument is simple. If a function is called by passing argument/s, those arguments are used by the function.
But if the argument/s are not passed while invoking a function then, the default values are used.
Default value/s are passed to argument/s in the function prototype.
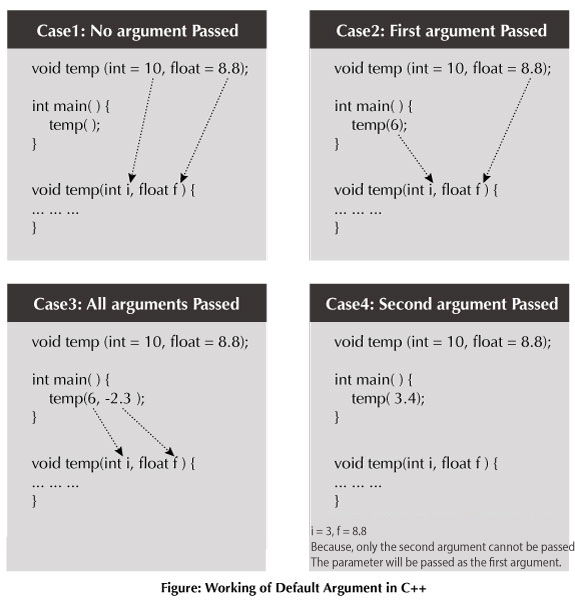
Working of default arguments

Example: Default Argument
// C++ Program to demonstrate working of default argument
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void display(char = '*', int = 1);
int main()
{
cout << "No argument passed:\n";
display();
cout << "\nFirst argument passed:\n";
display('#');
cout << "\nBoth argument passed:\n";
display('$', 5);
return 0;
}
void display(char c, int n)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
cout << c;
}
cout << endl;
}
Output
No argument passed: * First argument passed: # Both argument passed: $$$$$
Common mistakes when using Default argument
void add(int a, int b = 3, int c, int d = 4);
The above function will not compile. You cannot miss a default argument in between two arguments.
void add(int a, int b = 3, int c, int d);
The above function will not compile as well. You must provide default values for each argument after b.
In this case, c and d should also be assigned default values.
If you want a single default argument, make sure the argument is the last one.void add(int a, int b, int c, int d = 4);
- No matter how you use default arguments, a function should always be written so that it serves only one purpose.
Comments
Post a Comment